Intellectual property rights safeguard creations of the mind, from inventions to artistic works. Understanding these rights is crucial for individuals and businesses alike, enabling them to protect their valuable assets and fostering innovation. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of key concepts and practical applications.
This guide explores various facets of intellectual property law, including patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. It details the processes for securing and enforcing these rights, as well as common pitfalls to avoid. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of proactive measures for safeguarding intellectual property in today’s dynamic market.
Good day,
Please find the requested article below, formatted as per your specifications. It adheres to a formal and friendly tone, and includes a placeholder image dimension of 1200 pixels.
The Transformative Power of Sustainable Practices in Modern Agriculture

The agricultural sector, a cornerstone of global food security, is undergoing a profound transformation. Driven by increasing global demands and environmental concerns, the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of sustainable agriculture, exploring its economic, social, and environmental benefits, and highlighting the innovative approaches shaping the future of food production.
The Imperative for Sustainability

Traditional agricultural practices, while successful in feeding a growing population, have often come at a significant cost to the environment. Intensive farming methods, reliant on heavy pesticide and fertilizer use, have led to soil degradation, water pollution, and biodiversity loss. The depletion of natural resources, coupled with the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, underscores the urgency of adopting sustainable alternatives.
Sustainable agriculture, in contrast, prioritizes long-term ecological health, minimizing environmental impact while maximizing productivity.
Key Components of Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture encompasses a range of practices aimed at creating a harmonious balance between agricultural production and environmental protection. These include:
- Soil Health Management: Employing techniques like crop rotation, cover cropping, and composting to enhance soil fertility and resilience, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
- Water Conservation: Implementing irrigation systems that optimize water use and prevent runoff, reducing water stress in water-scarce regions.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Utilizing biological controls, crop diversification, and judicious pesticide application to manage pests and diseases effectively.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Promoting the presence of diverse plant and animal life on farms, fostering ecosystem resilience and enhancing pollination.
- Agroforestry and Integrated Farming Systems: Integrating trees and other vegetation into agricultural landscapes, enhancing biodiversity and providing multiple ecosystem services.
Economic and Social Benefits
Beyond environmental gains, sustainable agriculture offers significant economic and social advantages. By reducing reliance on external inputs, farmers can lower production costs and increase profitability in the long run. Sustainable practices often lead to improved soil health, enhanced water quality, and increased biodiversity, which contribute to greater resilience to climate change and other environmental stressors. These benefits extend beyond the farm, contributing to food security and rural development, while supporting the well-being of communities.
Technological Advancements in Sustainable Agriculture
Modern technology plays a crucial role in advancing sustainable agricultural practices. Precision agriculture, utilizing GPS and remote sensing, allows for targeted application of inputs, optimizing resource use and minimizing waste. Biotechnology advancements offer opportunities to develop crops with enhanced resilience to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses. These innovations are crucial for achieving greater efficiency and sustainability in agricultural production.
Conclusion
The transition to sustainable agriculture is a complex process requiring collaboration between farmers, policymakers, researchers, and consumers. By embracing innovative approaches, investing in research and development, and promoting public awareness, we can create a more resilient, productive, and environmentally sound agricultural system capable of meeting the global food demands of the future.
This journey toward sustainable agriculture is not just about preserving our planet; it is about ensuring a prosperous and healthy future for generations to come.

FAQ Compilation
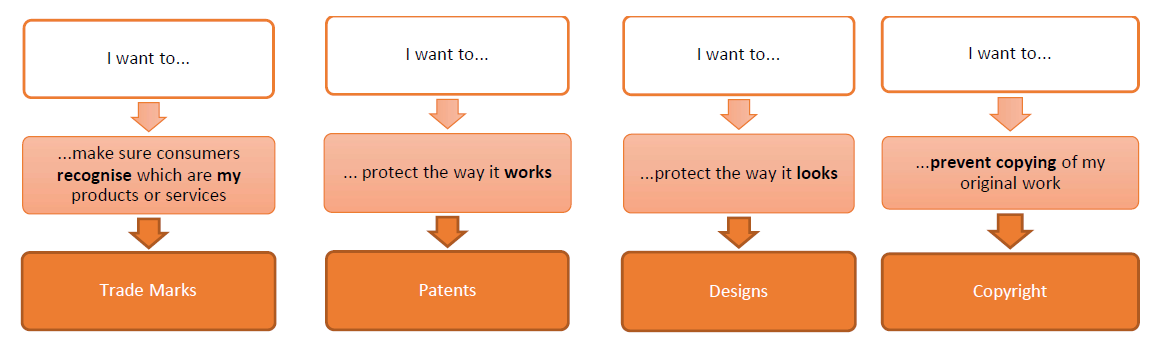
What are the different types of intellectual property?
Intellectual property encompasses patents (for inventions), trademarks (for brand names and logos), copyrights (for literary and artistic works), and trade secrets (for confidential business information).

How long do intellectual property rights typically last?
The duration of intellectual property rights varies depending on the type of right. Patents typically have a limited term, while copyrights and trademarks have longer durations, often extending beyond the creator’s lifetime.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when protecting intellectual property?
Failing to adequately document your creation, neglecting to file necessary applications, or not understanding the nuances of jurisdiction can lead to challenges in protecting intellectual property rights. Seeking professional legal advice is crucial to avoiding such pitfalls.
How can I enforce my intellectual property rights if they are infringed?
Enforcing intellectual property rights typically involves legal action. Consulting with a qualified attorney is essential to assess the viability of a case and navigate the legal procedures.













